The US options trading market is widely recognized as one of the most dynamic and liquid in the world, offering investors a wide array of strategic tools to manage risk, generate income, or gain leveraged exposure.( However, it's important to note that options also carry the potential for significant losses, and leveraged strategies should be approached with caution.)
For Hong Kong investors, participating in this market opens the door to global opportunities. However, navigating US options trading with confidence requires a solid understanding of options trading rules and structure. This guide outlines the key regulations and market practices every investor from Hong Kong should be aware of—so you can trade smarter!
Overview of the US Options Market Structure
US options trading is tightly regulated to protect market integrity and investor interests.
Two key authorities oversee the market:
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): SEC is a financial regulator created under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. It oversees stock markets, brokers, and public companies to ensure transparency, prevent fraud, and protect investors[1].
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC): Established in 1974, the CFTC is a US agency that regulates derivatives markets, including futures, options, and swaps, to ensure fair trading and protect against fraud and manipulation[2].
Understanding options trading rules starts with recognizing the role of these regulators in maintaining a fair and orderly market.
Types of Options
Call Options: The right to buy the underlying asset at a set price within a specified time.
Put Options: The right to sell the underlying asset under similar conditions[3].
The terms "American-style" and "European-style" options refer to different options trading rules around exercise timing. American options can be exercised anytime before expiration, while European options are only exercisable at expiry[4].
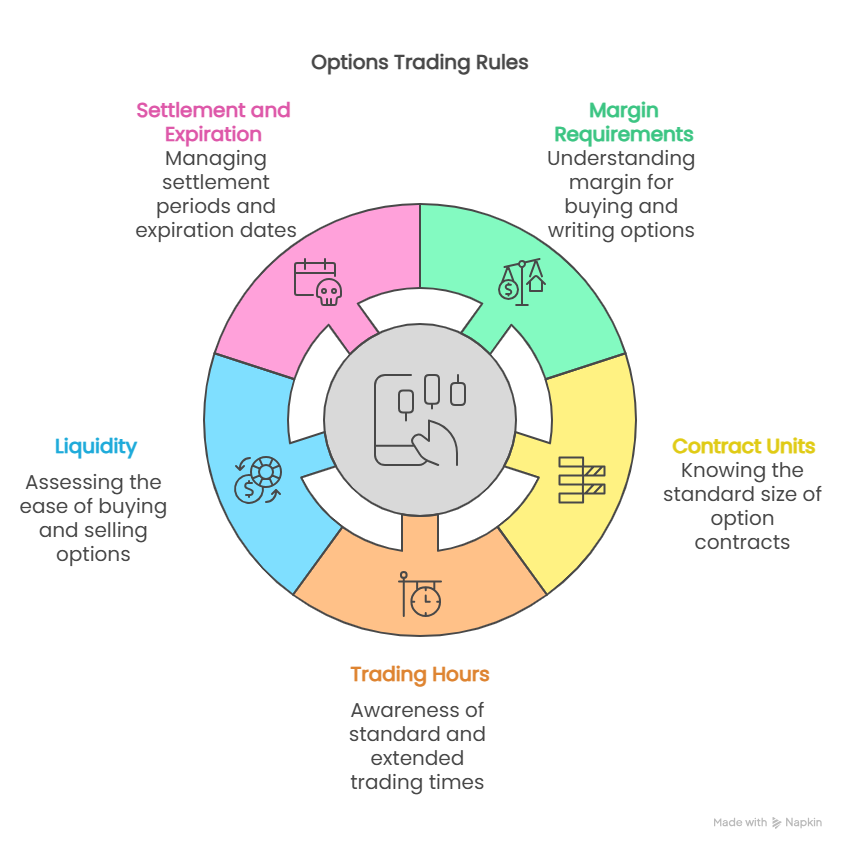
Core Options Trading Rules to Know
1. Margin Requirements
When buying options, investors pay the full premium upfront and no margin is required. However, when writing options—especially uncovered (naked) calls or puts—margin is necessary to ensure the writer can meet potential obligations[5].
The initial margin is typically calculated as the premium received plus an additional percentage of the underlying security’s market value, depending on the risk and position type. Maintenance margin may also be required to keep positions open[6].
These options trading rules are governed by The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and Regulation T, though each online brokerage may apply stricter policies.
2. Option Contract Units
One of the basic options trading rules that every investor must understand is the concept of option contract size. In the US options market, a standard option contract typically represents 100 shares of the underlying stock[7]. This means that when you buy or sell one options contract, you are actually trading rights or obligations tied to 100 shares.
It’s important to be aware of this standard lot size because it affects the total value of the contract and your potential exposure. For example, buying a call option priced at $2 means paying $200 in total (i.e., $2 × 100 shares).
3. Trading Hours
The standard trading hours for US options are 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST (9:30 PM to 4:00 AM HKT)[8]. Some online brokerages like Tiger Brokers, offer extended hours of trading, enabling investors to react to earnings reports or macroeconomic news outside the regular session.
4. Liquidity Considerations
Liquidity is vital in following options trading rules, as it affects pricing and execution. Highly liquid options typically exhibit narrow bid-ask spreads, high open interest and substantial trading volume. Conversely, illiquid options often have wider spreads and lower open interest, leading to potential slippage and suboptimal pricing[9].
Investors should also consider stock option lot size and how it affects their ability to enter or exit positions efficiently.
5. Settlement and Expiration
Settlement Period: US equity options settle on a T+1 basis (trade date plus one business day)[10].
Expiration: Most standard monthly options expire on the third Friday of each month. However, if this day falls on a market holiday, the expiration shifts to the preceding Thursday. Additionally, weekly and quarterly options have their own specific expiration schedules[11].
Traders must follow these options trading rules carefully, especially near expiration, to avoid unintended assignment of American-style options.
How Tiger Brokers Enhances Your US Options Trading
At Tiger Trade, we provide tools and features tailored to Hong Kong investors involved in US options trading. As a trusted online trading platform, we help users adhere to options trading rules with the following:
Comprehensive Option Analytics: Tiger Trade provides tools such as unusual options activity tracking, option chains, and built-in strategy analysis features that help users observe market dynamics and structure trades accordingly.
Support for Multi-leg Orders: Investors can access combination (multi-leg) order functionality, which allows the execution of complex strategies in a single order. For eligible combinations, Tiger Trade may offer margin relief, potentially reducing capital requirements.
Multiple Strategy Templates: A variety of commonly used options strategies—such as spreads, straddles, and iron condors—are available for users to reference and apply based on their own market outlook.
Cost-Effective Trading: The platform offers zero-commission trading for US options(time-limited) and provides free Level 1 market quotes, helping users control transaction-related costs.
Conclusion
US options trading is a powerful way to diversify your investment strategy, but it requires careful attention to market structure and trading rules.
With our advanced tools, educational resources, and local support, you’re well-positioned to explore opportunities in one of the world’s most sophisticated options markets.
Reference
What Is the Securities Exchange Act of 1934? Reach and History. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/seact1934.asp (Accessed: 8th, May)
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) Overview. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cftc.asp (Accessed: 8th, May)
Options Basics. Available at: https://www.optionseducation.org/optionsoverview/options-basics (Accessed: 8th, May)
What is the difference between American-style and European-style options? Available at: https://www.optionseducation.org/news/what-is-the-difference-between-american-style-and (Accessed: 8th, May)
Option Margin: Definition, Requirements, How To Calculate. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/o/option-margin.asp (Accessed: 8th, May)
Initial Margin: Definition, Minimum Requirements, Example. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/initialmargin.asp (Accessed: 8th, May)
Options Contract: What It Is, How It Works, Types of Contracts. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/o/optionscontract.asp (Accessed: 8th, May)
Nasdaq - Options Market Hours. Available at: https://www.nasdaqtrader.com/Trader.aspx?id=optionshours (Accessed: 8th, May)
How Options Liquidity Impacts Trading. Available at: https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/how-options-liquidity-impacts-trading-2017-10-30 (Accessed: 8th, May)
Preparing for T+1 Settlement. Available at: https://business.bofa.com/en-us/content/preparing-for-t1-settlement.html (Accessed: 8th, May)
Options Expiration: All You Need to Know Available at: https://www.tastylive.com/concepts-strategies/options-expiration (Accessed: 8th, May)
Disclaimer
Investing involves risks, and past performance does not reflect future results. Tiger Brokers makes no warranty as to the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of the information, and none of this constitutes any investment advice or opinion. Screenshots are provided for illustrative purposes only. Before investing, please consider your own risk tolerance and refer to the relevant risk disclosures for more details.